Vaginal yeast infection is a common health issue that affects many women at some point in their lives. These infections are primarily caused by an overgrowth of the Candida fungus, with Candida albicans being the most prevalent species involved. While a Vaginal yeast infection can be uncomfortable and distressing, they are largely treatable.
Prevalence of Vaginal Yeast Infection
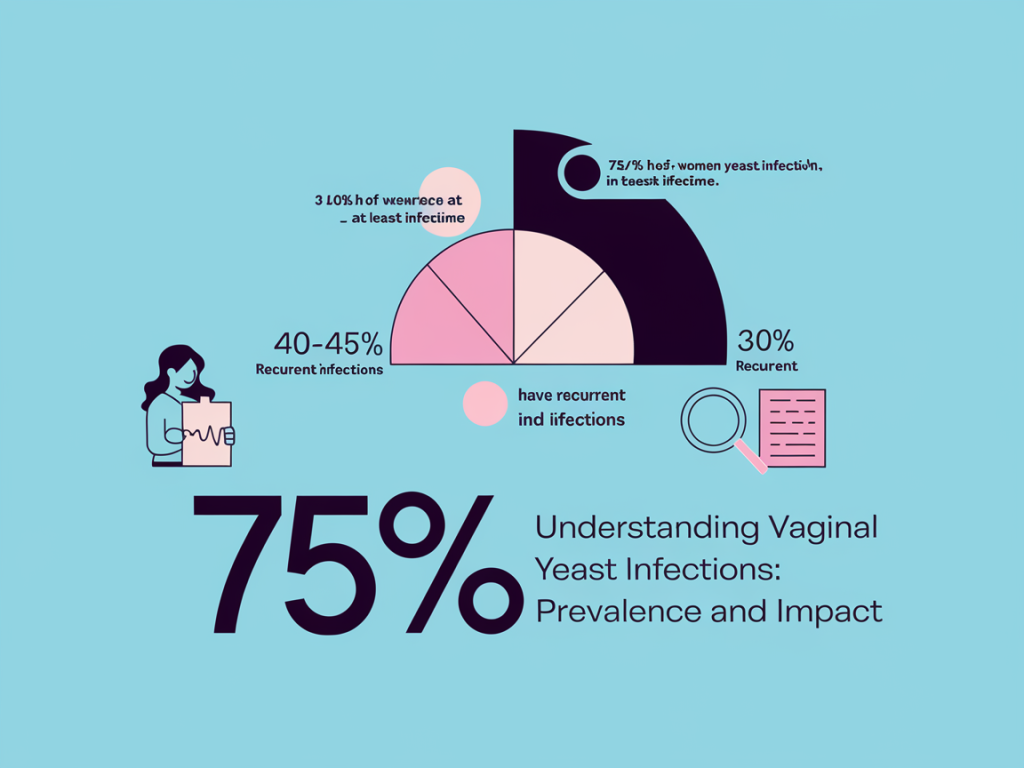
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about 75% of women will experience at least one vaginal yeast infection in their lifetime, and approximately 40-45% will have two or more episodes. Factors such as hormonal changes, lifestyle behaviors, and medical conditions make these infections a frequent concern for many women. These infections are typically caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida, which is normally present in small amounts in the vagina. Certain factors can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria and yeast, leading to an overgrowth of Candida. Common triggers include:
1. Antibiotic Use: Antibiotics can kill beneficial bacteria in the vagina, allowing yeast to flourish.
2. Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones due to menstruation, pregnancy, or hormonal contraceptives can increase the risk of Vaginal yeast infection.
3. Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to elevated glucose levels in the bloodstream and vaginal secretions, creating an environment conducive to yeast growth.
4. Immune System Suppression: Conditions that weaken the immune system, such as HIV/AIDS or medications like chemotherapy, can make women more susceptible to Vaginal yeast infection.
5. Lifestyle Factors: Certain lifestyle choices, such as wearing tight-fitting clothing, using scented hygiene products, or douching, can also disturb the vaginal environment.
Symptoms of a yeast infection typically include itching, burning, and discharge that may range from cottage cheese-like to watery. While these infections can be uncomfortable, they are often easily treatable with antifungal medications, which are available over-the-counter or by prescription.
The Role of Candida Fungus
Candida is a type of yeast that naturally resides in the body, including the vaginal area, digestive tract, and on the skin. Under normal circumstances, this fungus coexists with other microorganisms, and the body’s immune system keeps its growth in check. However, certain conditions can lead to an overgrowth of Candida, resulting in a yeast infection. This overgrowth can occur due to various factors, including antibiotic use, which can disrupt the balance of bacteria that normally keep Candida in check. Other triggers include hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy or menstruation, a weakened immune system due to illness or stress, and uncontrolled diabetes, which can create a more favorable environment for yeast to thrive.
Symptoms of a Candida overgrowth, or yeast infection, can vary but often include itching, irritation, and discomfort in the affected area. In the case of vaginal yeast infections, women may also experience a thick, white discharge resembling cottage cheese and a burning sensation during urination or intercourse.
To manage and treat a Candida overgrowth, healthcare providers may recommend antifungal medications, which can be prescribed in oral or topical forms. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as adopting a balanced diet low in sugar and refined carbohydrates, wearing breathable clothing, and maintaining good hygiene can help restore the natural balance of microorganisms in the body.
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment if you suspect a yeast infection or experience recurrent symptoms. Understanding the underlying causes and taking proactive steps can help prevent future occurrences and maintain overall health.
Symptoms of Vaginal Yeast Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of a vaginal yeast infection is crucial for timely treatment and relief. Common symptoms include:
– Itching and Irritation: This is often the most prominent symptom, with many women describing it as intense and persistent.
– Burning Sensation: Discomfort may arise, especially during urination or intercourse.
– Vaginal Discharge: The discharge typically appears thick, white, and odorless, resembling cottage cheese.
Less Common Symptoms
In addition to the more typical symptoms, some women may experience:
– Pain during sexual intercourse
– Redness and swelling of the vulva
– A rash around the vaginal area
While these symptoms are usually indicative of a yeast infection, it’s important to note that they can also signal other, more serious conditions. For instance, if symptoms are accompanied by a strong odor, abnormal discharge color, or significant pain, it might indicate bacterial vaginosis or a sexually transmitted infection. Seeking medical advice in such cases is essential.
Causes and Risk Factors
Vaginal yeast infections generally occur due to an overgrowth of Candida albicans. Several factors can lead to this imbalance:
Primary Causes
Antibiotic Use: Antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina, reducing the number of beneficial bacteria that help keep Candida in check.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as those experienced during menstruation, pregnancy, or hormone replacement therapy, can create an environment that favors yeast overgrowth.
Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to higher levels of glucose in the vaginal secretions, providing an ideal environment for Candida to thrive.
Immune System Suppression: Individuals with compromised immune systems, whether due to conditions like HIV/AIDS, cancer treatments, or other factors, may be more susceptible to Vaginal yeast infection.
Moisture and Heat: Wearing tight-fitting clothing or synthetic fabrics that trap moisture can create a warm, damp environment conducive to yeast growth.
Diet: A diet high in sugar and refined carbohydrates may contribute to an increase in Candida levels.
Personal Hygiene Products: The use of scented soaps, douches, and feminine hygiene sprays can disrupt the natural vaginal flora and lead to irritation, promoting infections.
Sexual Activity: Although yeast infections are not classified as sexually transmitted infections, sexual activity can alter the vaginal environment, making it more susceptible to yeast overgrowth.
Understanding these factors can help in preventing yeast infections and managing overall vaginal health. If recurrent infections occur, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance.
Risk Factors
– Tight Clothing: Wearing tight-fitting clothes, particularly made of synthetic materials, can create a warm, moist environment conducive to yeast overgrowth.
– Poor Hygiene: Inadequate personal hygiene can lead to imbalances in the vaginal flora.
– Dietary Choices: High sugar diets may contribute to the frequency of infections.
Misconceptions
It is important to debunk the myth that vaginal yeast infections are sexually transmitted. While they can occur in sexually active individuals, they are not considered sexually transmitted infections. Yeast infections, primarily caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida, can occur for various reasons that are unrelated to sexual activity. Factors such as hormonal changes, antibiotics, a weakened immune system, and environmental conditions like moisture and warmth can contribute to the development of a vaginal yeast infection.
Women may experience these infections due to factors like menstruation, pregnancy, or contraception use, which can alter the vaginal environment. Additionally, certain lifestyle choices, such as wearing tight or non-breathable clothing and poor dietary habits, can also increase the risk.
While sexual activity can potentially introduce bacteria that might disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms in the vagina, the presence of a yeast infection is not a reflection of promiscuity or lack of hygiene. It’s essential for individuals experiencing symptoms—such as itching, burning, or abnormal discharge, to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment, rather than attributing the infection to sexual behavior.
Understanding this distinction helps reduce stigma and encourages individuals to seek help without fear of judgment, fostering better sexual and reproductive health overall.
Diagnosis of Vaginal Yeast Infections

When it comes to diagnosing a vaginal yeast infection, healthcare professionals typically follow these steps:
1. Pelvic Examination: A thorough pelvic exam allows the clinician to observe symptoms and identify irritation or discharge.
2. Lab Tests: A sample of vaginal discharge can be taken for laboratory analysis. This process helps confirm the presence of Candida and rule out other complications such as bacterial vaginosis or sexually transmitted infections.
An accurate diagnosis is crucial, as treating the wrong condition could lead to worsening symptoms or complications.
Treatment Options
Over-the-Counter Antifungal Treatments
Many women find relief using over-the-counter antifungal options available at pharmacies, including:
– Antifungal Creams: Applied externally or internally.
– Ointments: Target the infected area directly.
– Suppositories: Inserted into the vagina, providing localized treatment.
These treatments are often effective for mild to moderate infections.
Prescription Medications
For more persistent or severe infections, healthcare providers may prescribe:
– Oral Antifungals: Medications like fluconazole are commonly prescribed for quick and effective treatment.
– Topical Prescription Medications: Stronger antifungal creams or vaginal tablets may also be recommended.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes

While medical treatments are effective, some women may seek relief through home remedies. Options include:
– Probiotics: Supplements or probiotic-rich foods like yogurt may help restore healthy vaginal flora.
– Dietary Adjustments: Reducing sugar intake can help manage yeast overgrowth.
– Appropriate Hygiene Practices: Daily bathing and careful choice of personal hygiene products can prevent infection recurrence.
Importance of Completing Treatment
Regardless of the treatment chosen, completing the full course is essential to avoid recurrence and ensure full resolution of the infection. It is crucial to adhere to the prescribed dosage and duration, as stopping treatment prematurely can allow the remaining pathogens to survive and potentially develop resistance. This not only jeopardizes the individual’s health but can also contribute to broader public health issues.
In addition to following the treatment regimen, patients should remain vigilant for any lingering symptoms or new developments, as these may indicate that the infection is not fully resolved. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers can help monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Moreover, practicing good hygiene and taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of future infections. This may include avoiding sharing personal items, maintaining a clean environment, and following guidelines for safe food and water consumption.
Educating oneself about the infection, its transmission methods, and ways to strengthen the immune system can also empower individuals to take proactive steps towards their health. Remember, collaboration with healthcare professionals is key to achieving the best outcomes and fostering a healthier community.
Prevention Tips
To reduce the risk of developing a vaginal yeast infection, consider the following preventive strategies:
– Wear Breathable Underwear: Cotton underwear allows for ventilation, reducing moisture buildup.
– Avoid Douching: Douching can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria, promoting yeast overgrowth.
– Maintain Hygiene: Regular bathing and proper genital hygiene are crucial.
– Watch Your Diet: A balanced diet low in sugar and rich in whole foods may support overall vaginal health.
– Manage Stress: Stress can affect your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
When to See a Doctor
While most Vaginal yeast infection can be treated at home, it’s necessary to see a healthcare provider in the following cases:
– Recurrent Infections: Frequent infections (more than 4 a year) may indicate an underlying health issue that needs addressing.
– Severe Symptoms: Intense pain, swelling, or systemic symptoms like fever warrant medical attention.
– Uncertainty About Diagnosis: If symptoms are unusual or persist despite treatment, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Vaginal yeast infection is a common, manageable, and treatable conditions that many women experience. By understanding their symptoms, causes, and treatment options, women can take proactive steps to maintain their vaginal health. Preventative measures and early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of recurrent infections, making it essential to be informed and vigilant about one’s health.
FAQ Section
1. Are vaginal yeast infection contagious?
No, vaginal yeast infections are not contagious and cannot be spread from one person to another.
2. Can I use tampons during a yeast infection?
Using tampons during a yeast infection is generally safe, but it’s advisable to use sanitary pads as the discomfort may increase.
3. How long does a yeast infection last?
With proper treatment, symptoms usually resolve within a few days. If symptoms persist, it may be necessary to consult a healthcare provider.
4. Can I use probiotics to prevent yeast infections?
Probiotics may help restore the natural balance of vaginal flora and could be beneficial in preventing yeast infections, especially for those prone to recurrent issues.
5. Is it normal to have a yeast infection during pregnancy?
Yes, hormonal changes during pregnancy can make women more susceptible to yeast infections. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for safe treatment options during pregnancy.
6. Can lifestyle changes help prevent yeast infections?
Absolutely! Maintaining good hygiene, wearing breathable clothing, and managing your diet can significantly lower the risk of developing yeast infections.
—
By being informed about vaginal yeast infections, what they are, how to recognize them, and how to treat and prevent them, women can take control of their health and well-being. If in doubt or experiencing recurrent issues, consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended.